ENVIRONMENTAL LEVEL
Environmental Protection and Impact
Borusan is dedicated to conducting its activities in an environmentally sound and safe manner, adhering to legal requirements and it adopts sustainable practices to efficiently use natural resources and energy. This ethos is an integral aspect of our business operations, and we anticipate our suppliers to uphold similar standards.
Environmental Management Systems
Borusan expects its suppliers to comply with national and international environmental standards and regulations, possess effective and certified environmental and energy management systems to manage their environmental impacts, and establish robust policies, processes, and procedures.To align with Borusan's expectations within the environmental management systems domain, it suffices for suppliers to possess globally recognized standards and certifications (e.g., ISO 14001, ISO 14064, EMAS). In the absence of such certifications, suppliers are required to maintain environmental policies and procedures. The Environmental Policy delineates the company's overarching objectives and trajectory concerning its environmental performance, endorsed by senior management. It establishes a framework for the company's initiatives to adhere to relevant legal and other stipulations, reduce environmental impact, conserve resources, and minimize costs, while considering the environmental implications of the company's operations, products, and services.
Given the diverse nature of activities within our supplier network in the Borusan ecosystem, the emphasis placed on environmental management may vary among suppliers.
Management of Restricted Chemicals:
Our suppliers are required to adhere to national and international regulations and other stipulations concerning banned and/or restricted chemicals. The key requirements for compliance include:• Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) - Directive 2002/95/EC, abbreviated as RoHS 1, is a European Union regulation restricting the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment.
• Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) - REACH is a European Union regulation. It addresses the production and utilization of chemicals and their potential impact on human health and the environment.
• Toxic Substances Control Act (US EPA TSCA) - TSCA is a US federal law adopted by the United States Congress and administered by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), regulating chemicals not governed by other United States federal laws. It covers chemicals already in commerce and the identification of new chemicals.
• Regulation on Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (KKDIK) - Published by the Turkish Ministry of Environment and Urbanization, KKDIK addresses the registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals for safe use.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
Suppliers are expected to implement process improvements and adopt practices to enhance energy efficiency, thereby reducing their carbon footprint. Furthermore, suppliers are mandated to provide transparency regarding their use of renewable energy, where available, and explore options for transitioning to renewable energy sources within the scope of clean energy utilization. To meet the expectations outlined under the energy efficiency sub-heading, Borusan requires its suppliers to prioritize energy efficiency in their operational and corporate endeavors. Suppliers are expected to implement practices that support energy efficiency and ensure that periodically monitored energy consumption data can be reported by relevant units. Specifically, suppliers are expected to monitor and report the amount of primary energy consumption, including oil, coal, natural gas, and electricity consumption. This forms one of the initial steps in energy management activities mandated for suppliers. Projects aimed at enhancing efficiency and/or new investments focused on achieving savings, developed within the framework of each operational mechanism that is monitorable and manageable, are also addressed within this context.
To fulfill the expectations outlined under the renewable energy sub-heading, Borusan requires its suppliers to develop investment and efficiency-oriented projects capable of meeting their current energy consumption needs from alternative natural resources. These projects should also serve as additional energy sources in their operational processes. To elaborate further, renewable energy is derived from natural resources such as solar, wind, biomass, geothermal, and wave energy. Suppliers are encouraged to explore options for generating renewable energy on their operational campuses through means like solar panels and wind power plants, or by purchasing renewable energy from third parties.
Borusan expects its suppliers to monitor their activities focused on both energy efficiency and renewable energy use using environmental performance indicators. These activities should be based on sustainable data sources, with annual assessments of improvements and developments. Additionally, suppliers are urged to have an environmental strategic goal that is aligned with Borusan's company values.
Carbon Emissions
At Borusan, we are committed to fostering healthy ecosystems through our carbon-free business model objective. Accordingly, we undertake projects aimed at effectively managing and reducing emissions and manage our operations within the scope of our goal to minimize our carbon footprint. We expect our suppliers to similarly calculate their carbon emission levels and set strategic targets for reduction in alignment with our objectives.
Carbon Emission Amount
Carbon emission amounts should be transparently provided by suppliers for their own operations and, where applicable, for production-oriented activities.The term "carbon footprint" refers to the total greenhouse gas emissions stemming from the key activities of organizations or individuals, such as transportation and electricity consumption, measured in units of carbon dioxide. Calculations for carbon footprints utilize various globally accepted methodologies and standards. Among these methodologies that address the six main greenhouse gases (CO2, CH4, N2O, PFc, HFc, SF6) within the scope of the Kyoto Protocol, those issued by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) as well as the GHG Protocol, and ISO 14064 can be listed as the leading standards.
When calculating carbon footprint emissions, it is crucial to establish the boundaries of the data sources as a preliminary step. It is imperative to gather data on operational activities, calculate emission factors and global warming potentials, and report them using a common language in accordance with globally accepted standards. Organizations should acknowledge that emission factors may vary between countries and evolve over time. Emission factors can be drawn from a wide range of sources including IPCC guidelines and WBCSD's GHG Protocol.
Scope 1 emissions refer to direct emissions from the reporting organization's operations, production facilities, or transportation vehicles (e.g., natural gas, coal, gasoline, diesel, LPG consumption).
Scope 2 emissions encompass non-direct emissions from electricity, steam, heating, and cooling purchased by the reporting organization. They are also referred to as energy indirect emissions.
Scope 3 emissions comprise emissions indirectly resulting from the activities of the reporting organization. This category describes greenhouse gas emissions from sources owned or controlled by other organizations due to an organization's activities. It typically refers to emissions from external stakeholders within the organization's value chain (e.g., fuel consumption of rental vehicles, emissions from organizations in the supply chain, emissions from the production of purchased materials).
Borusan expects its suppliers to provide transparent and reliable sources for carbon emission calculations, adhering to detailed shared guidelines, and to annually report this data using appropriate methodologies based on reference values.
Carbon Emission Reduction
Borusan mandates its suppliers to take effective measures and implement necessary practices by formulating plans to monitor, reduce, and manage both their direct and indirect CO2 emissions.
Organizations are required to identify strategic development areas, evaluate science-based targets, and define emission reduction measures as part of their carbon emission calculations. In line with the objectives to be set forth, suppliers are required to implement a range of new practices aimed at establishing carbon emission limits, ensuring adherence to the boundaries set within the framework of the applicable standards. Planned activities and/or investments are expected to be in alignment with the carbon emission reduction target established by the organization. Organizations must keep track of and monitor the implications of existing practices or new activities to be implemented in this direction. In this regard, Borusan expects its suppliers to annually report their carbon emission reduction projects, reduction rates, and development processes.
Circularity Understanding
At Borusan, we embrace a business model inspired by circular principles observed in nature. Accordingly, we have been designing conscious actions to integrate reuse, remanufacture, and rethinking into our production and service processes. Moreover, we expect our suppliers to align their production processes with circularity principles, aiming to establish climate-conscious systems not only within our own operations but also across our entire value chain.
Waste Management
Borusan encourages its suppliers to have a waste management procedure to ensure the accurate management of waste generated in their operational processes within the framework of relevant legislation and regulations. Our suppliers are also required to implement effective practices aimed at reducing environmental impact and minimizing waste generation in their operations. This includes preemptively preventing waste generation after resource utilization whenever feasible, as well as efficiently reusing, repurposing, and properly disposing of waste that cannot be prevented. Furthermore, it is imperative to segregate waste generated at the end of operational processes, minimizing potential environmental damage, and ensuring compliance with legal limits. Borusan urges all its suppliers, especially those involved in production operations, to prioritize recycling activities within the framework of waste management. In this regard, it is crucial for Borusan that companies achieve their zero waste targets as part of their strategic activities and annual practices, ensuring minimal potential damage to the environment.
It is also anticipated that sustainable products and labeling preferences be prioritized within the companies along the value chains of Borusan suppliers and with which they conduct their procurement activities. Therefore, Borusan suppliers are expected to prefer products that embrace a circular approach (environmentally friendly, bearing recycled or recyclable product labels, low carbon emission, etc.) in their purchasing decisions.
Product Design
Borusan urges its suppliers to develop environmentally friendly products aimed at minimizing the environmental impact throughout their entire life cycle, from production to final disposal. As such, companies are expected to prioritize eco-friendly, recycled, or recyclable designs with low carbon emissions, etc., in their existing product portfolio and to adopt a circularity approach. Suppliers are also requested to notify Borusan officials if they have the relevant product range.
Borusan guides its suppliers in creating a portfolio of sustainable products and shares examples of the characteristics of the main environmentally friendly product choices.
Examples of Sustainable Product Design
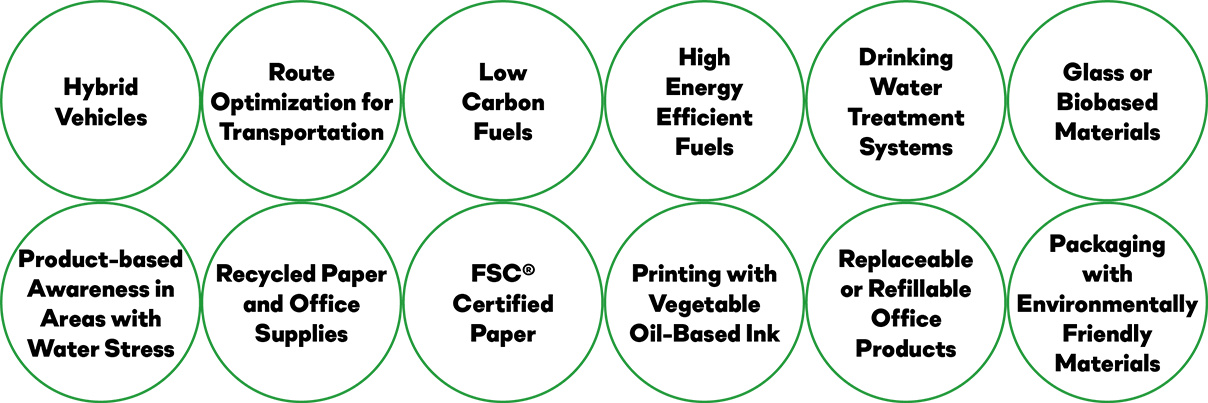
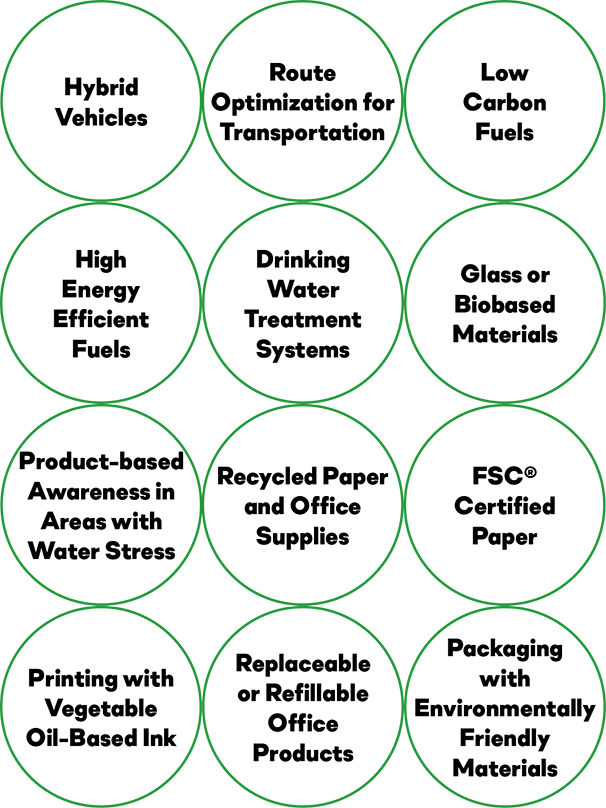
Examples of Sustainable Service Design
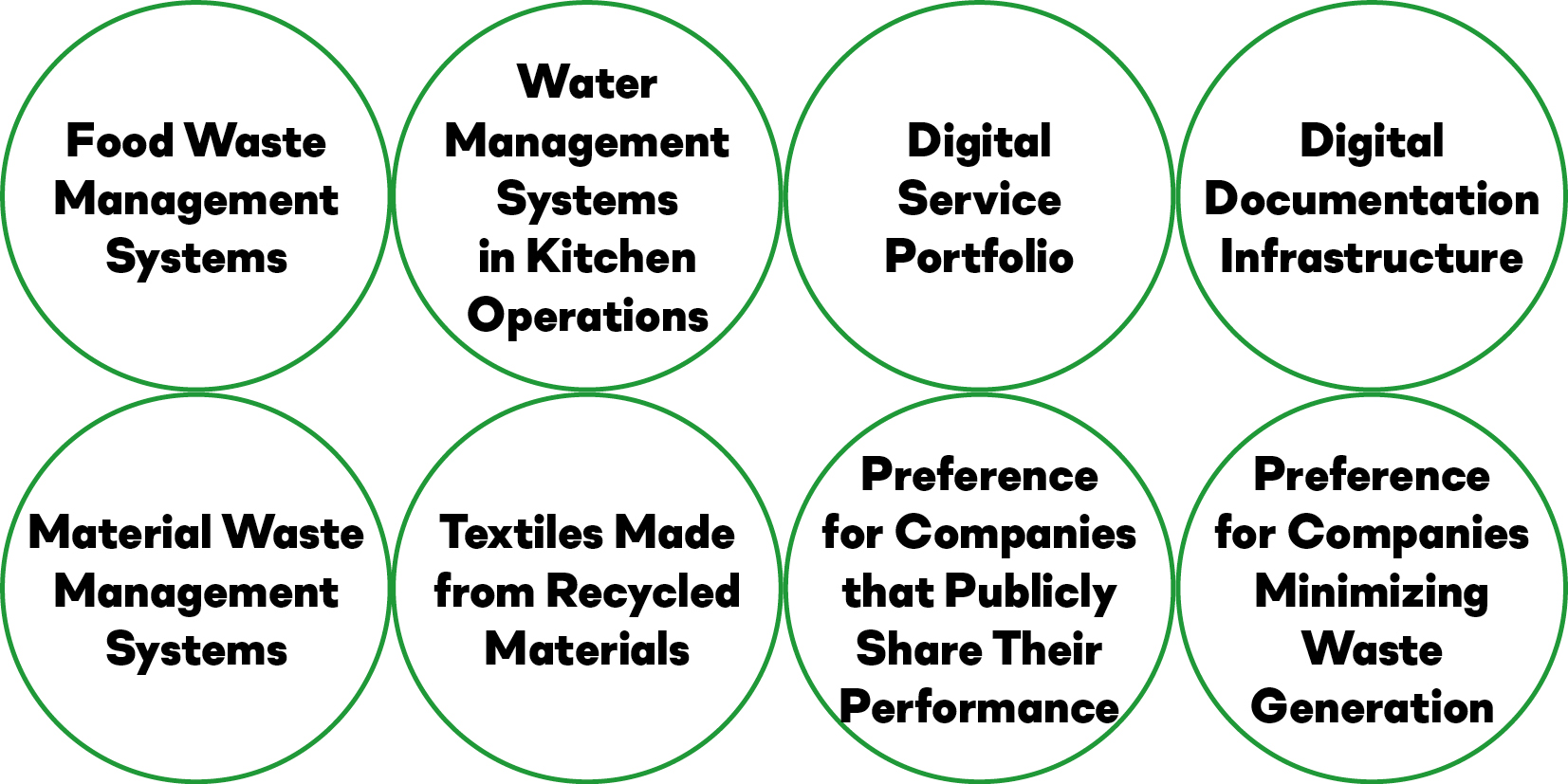

Material Utilization
Recognizing the limitations of natural resources, Borusan urges its suppliers to responsibly and efficiently utilize energy, water, and all types of raw materials and materials. They are also expected to develop more efficient production methods to optimize resource utilization. Throughout the production process, it is required to manage materials, raw materials, and resources in compliance with outlined procedures and regulations, including waste management, water management, and energy management.



